The information here is provided by courtesy of the Network's short online course - "An Introduction to Global Health".
Non-Communicable Diseases
Headline
Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) are responsible for around three quarters of all deaths around the world and they are increasing in their importance (Figure 1).
Figure 1

More than three quarters of global NCD deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
(See comparison between disease burdens of High and Low Income Countries)
The most important NCDs
80% of Non-Communicable Diseases are from 4 conditions (Figure 2)
- cardiovascular disease,
- cancers,
- chronic respiratory disease
- diabetes
Figure 2
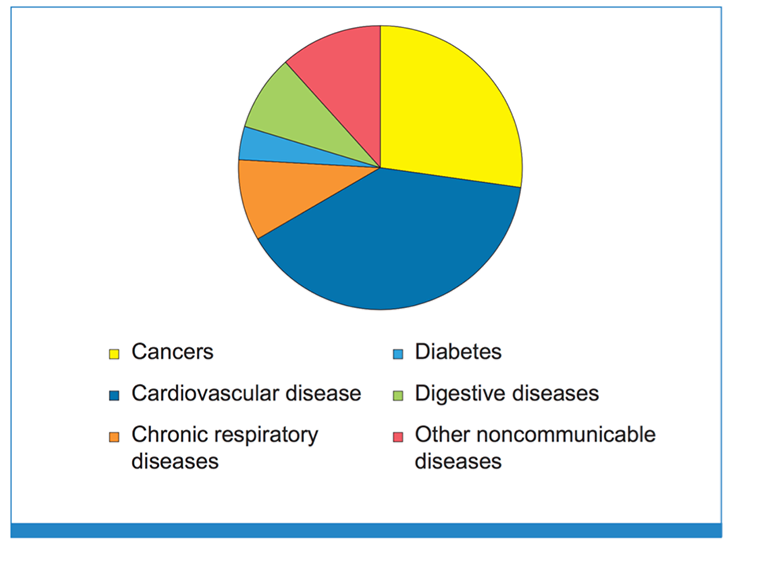
Source : WHO
Deaths from cardiovascular diseases and cancers are now the world leading causes of death (Figure 3)
Figure 3

Risk factors
The risk factors for Non-Communicable Diseases come predominantly from the lifestyle and physical environment that humans have created and not from the environment of the natural world (Figure 4).
Figure 4

Other risk factors include obesity, raised blood fats and sugars, which tend to come for a poor diet, and raised blood pressure.
Prevention
The things that individuals can do to reduce their own risk are
- not to smoke,
- reduce salt and alcohol intake,
- have a healthy diet
- take plenty of exercise.
However, countries need to invest in better management of NCDs. In addition to reducing air pollution, this includes detecting, screening, treating, and providing access to palliative care for people in need. High impact essential NCD interventions can be delivered through a primary health care approach to strengthen early detection and timely treatment. Evidence shows such interventions are excellent economic investments because, if provided early to patients, they can reduce the need for more expensive treatment.
What WHO is doing
UN Member States are committed to reduce by one thirds premature mortality from NCDs by 2030. WHO has a co-ordinating role and developed a "Global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013-2020" (see below). This has 9 targets that have the greatest impact on global NCD mortality and address prevention and management of NCDs.
Further reading
WHO Global Action Plan for the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases
WHO : WHO’s work on non-communicable diseases
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases
See also links provided in the sections on
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Cancers
- Tobacco
- Overweight and obesity




